Why Camel Milk is Bioavailable & Supplements Aren’t!
There is an increasing number of supplements and touted health remedies flooding the consumer market. Claims are made and waved in front of the eyes of potential buyers. Captured hearts buy the advertised capsules, powders or liquid – in high hopes of the solution to their every problem. But even with the $36.1 billion supplement sales recorded in 2017, the population doesn’t seem to be undergoing any “health revolution” as promised in the advertisements. In fact, major diseases like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes are still increasing.
So, if all these amazing health properties are compacted into the handful of supplements people consume daily, why are people still tapping their feet waiting on the results?
To make this clear, most supplements do have health benefits to offer and some make good on their promises. But many supplements are falling short of their boasts. The major reason for this is that the beneficial properties can’t pass through the multitude of barriers to have a positive effect on the body.
This leads us to the importance of using bioactive camel milk as a safe whole body support with its unique small sized health properties. Camel milk is ideal for human absorption because of its unique properties, liposomal delivery and similar structure to human milk.
Why Camel Milk is Bioavailable
Unlike supplements, camel milk is a whole food solution to getting a unique spectrum of health benefits. Camel milk is naturally optimized for human absorption lacking allergenic properties expressed in other milks. It is also the only natural source for nano-sized immunoglobulins, bioavailable insulin and human-like milk!
Stomach Acid
Camel milk’s properties are naturally bioavailable and optimized for the human body. Camel milk properties not only survive the stomach but have been studied to even protect against ulcers and support healing in the stomach. (9) Camel milks health factors are highly resistant to ph changes (2) and temperature (3).
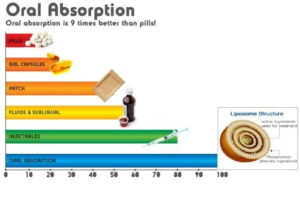
Phospholipids are a key liposome for absorption into the body, as it “melts” through the membrane and enters the body. Phospholipids or “liposomal delivery” is a key way to avoiding digestion and increased bioavailability. Phospholipids are so bioavailable they can even start making their way into the body before they even get to the stomach! The phospholipid content in camel milk is remarkably higher than all other milks (4).
The nano-sized antibody’s and insulin contained in camel milk are encapsulated in this Bi-lipid layer. [Image 1]
As the figure indicates, the liposomal carrier “literally” melts into the cell and hands off the intended nutrients. Camel milk immunoglobulins and insulin can pass directly into the cell without inhibition! This delivery system is a massive boon for anyone with a compromised digestion that can’t absorb well. A recent study in 2015 even identified and used camel milk liposomes as an anti-cancer drug delivery system (10).
Lab-made liposomal delivery is currently being utilized by forward-thinking supplement companies to increase absorption percentages. But camel milk has this technology naturally built into it!
Passing the Intestines
Camel milk is very bioactive but non-allergenic. Meaning, that its properties are recognized and utilized in the intestines but the human immune system doesn’t have a negative immune response.
Camel milk’s health factors can easily pass into the body without obstruction.
As with many common food sensitives, things like cow’s milk, chocolate, nightshades, peanuts, supplements etc. begin to be recognized as an invader. The body responds by stopping its entry and creating inflammation to stop the “invader”.
But camel milk due to its unique immune balancing properties and lack of common allergens like lactoglobulin and B-casein is a different kind of food. Surprisingly camel milk isn’t recognized by most human IgE antibody’s (largely in charge of allergic reactions) (7). There is even a popular trial of 8 kids with extreme allergies to almost all foods. The kids benefited from no traditional therapies and were given camel milk as a last resort. All 8 kids tolerated camel milk and “recovered fully” from their other food sensitivities! (8)
Intracellular & Extracellular
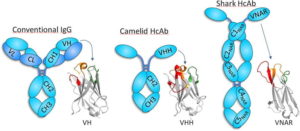
Most unique to camel milk is the ability to easily penetrate tissue and pass into cells for intracellular action. How is this possible? Well, one reason previously described is that camel milk has phospholipids. But unique to camel milk is that its immune proteins are nano-sized!
How unique is this? Camels milk is the only known natural source for bioavailable insulin. The nano-sized immune cells are only found in camels, llamas and shark fin.
Nano-sized immune proteins (IgG) is of most interest to researchers specifically due to its ability to be absorbed and move through the body’s barriers:
- Crosses the Blood-Brain-Barrier
- Thermal stability & pH tolerance
- Tissue & membrane Penetrating
- Passes easily through the membrane
- Promotes healthy chemokine output
- Broad antigen/intracellular binding
People have been using camel milk for a multitude of health benefits such as blood sugar optimization, immune balancing, detoxing, and much more. The many health benefits could be attributed to the camel milk’s unique ability to pass seamlessly through the human body.
Why your supplements aren’t absorbing
There are a multitude of reasons why your supplements aren’t absorbing. The road from the mouth all the way to cellular action is paved with no-nonsense barriers, choosey transporter proteins, and specifically designated enzymes. But obviously, we just want the nitty-gritty answer of “why isn’t my supplement working and how is camel milk different?”
The Stomach Acid
When a product is first ingested its first complication is with the stomach acid with an acidic environment between 1.5-3.5 ph. Most well-intended products are destroyed in this environment such as enzymes and probiotics.
An FSA Study by Dr. Gibson and colleagues found that in 35 probiotic strains from commercial products, only 4 of 35 strains would survive to enter the large intestines and those survivors would still have less than 50% survival rate. (1)
The common solution to stomach acid for supplements was to create a capsule to act as a “care package” delivery system. Unfortunately, most capsules are either gelatin or vegetable, which each run their own risks of contamination, toxicity, and not even being digested by the body!
Gelatin- Derived from the skin, bones, organs and connective tissues of animals including beef, pork, and fish.
Vegetable- HPMC, a Cellulose ether that is highly refined and chemically treated wood or tree trunks. Basically, a plastic.
Of course, this shouldn’t be shocking since the common over the counter supplement hasn’t had a good history. A recent Harvard study showed only 21% of store bought herbal supplements (one store showed only 4%!) had any trace of the advertised ingredients.
Passing the Intestines
When or if the supplement arrives at the intestines, it hits another tough barrier. At this point, we’re either absorbing directly into the bloodstream, or we’re leaving our hard-spent money in the toilet. If it’s a probiotic, it’ll obviously have a different destination.
In our intestinal lining, we have countless microvilli tightly packed with tiny openings to let in broken down (digested) and needed nutrients. These small tight junctions act like a TSA security check, scanning individuals and deciding who gets to come through.
The tight junctions are largely a useful safeguard against toxins and harmful bacteria from having an unchecked party in your body. But this is bad for most supplements. Supplements sometimes aren’t broken down enzymatically, not recognized as friendly by the intestinal proteins and are too large to enter the tight junction.
Intracellular & Extracellular
If the Intestinal barrier deems the compound nutritionally “worthy” of entering, then it passes into the bloodstream. Then what? The end? Not really…
Most nutrients need to pass into tissue and organs to have the intended effect on the body. A good example is the body’s innate powerhouse antioxidant, Glutathione. It works extracellularly (outside the cell) or intracellularly (inside the cell). People will take massive doses of glutathione; it’ll clean up outside the cell but never get inside of the damaged cells to do the real work. People continue to have oxidative stress and reduced cellular ATP production even though they’re “technically” taking something that should help.
Another issue that entire books can be written on is the form of nutrient and if it’s being utilized. When you start to takes supplements, you’ll see that each one may say “contains B12” but the “form” is different for each supplement. One may say Cyanocobalamin (synthetic) or Methylcobalamin. They are both B12 and you may be taking the right amount, but generally, the body doesn’t use the cheap Cyanocobalamin form.
If you learn anything from this long and complicated journey it’s this: don’t expect your body to absorb everything you put into it.
Why Camel Milk is Bioavailable and Supplements Aren’t: Conclusion
Bioavailability is becoming a major topic of conversation today. Consumers are recognizing the importance for more effective supplements on the market. Nutraceutical companies are working hard in the lab to manufacture high absorption rates and more effective supplements.
As is common, supplement companies backtrack to nature’s many secrets and puzzle over why their synthetic nutrients don’t work. The “top of the line” supplements use natural processes and compounds already available in nature.
We trust in food because it’s bioactive. The body knows what to do with an organic and naturally structured food. Once it becomes synthetic or needs to be made in a lab we risk either no response at all or an all-out immune response to an expected “foreign body”
Camel milk is not just a “food” though. Through painstaking evolution, camels adapted to one of the harshest environments and created an equally potent super milk. Camels did this to protect and build their baby calf’s immune system and natural hormonal system. As we begin to enter our own increasingly harsh environment of toxins, chemicals, and physical/psychological stress we look back to nature for an answer.
Camel milk was used as an ancient remedy for many years by the nomads of the deserts. Through science, we see the body prefers bioavailable and safe camel milk properties over harmful synthetic supplements.
CITATIONS
- The FSA study w/ Reading University G.R. Gibson, Dr. G. Rouzaud, Dr. J.Brostoff, and Dr. N. Rayment
- INSULIN IN MILK – A COMPARATIVE STUDY OLGA ZAGORSKI, ARIEL MAMAN, AVRHAM YAFEE, A. MEISLES, CLARA VAN CREVELD AND REUVEN YAGILFaculty of Health Sciences, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, P.O Box 653, BEERSHEVA 84105, Israel International Journal of Animal Science 13, p. 241-244, 1998
- Camel milk is more heat resistant than cow’s milk U. Wernery, Brigette Hanke, F. Braun and Bobby Johnson Central Veterinary Labs, Dubai, UAE | MUVA Kempten, Qualitats-und Laborzentrum, Germany Milchwissenschaft 58 (5/6) 2003
- Phospholipid fingerprints of milk from different mammalians determined by 31P NMR: towards specific interest in human health Cyrielle Garcia, Norbert W. Lutz, Sylviane Confort-Gouny, Patrick J. Cozzone, Martine Armand, Monique Bernard PII: S0308-8146(12)00960-0 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.111 Reference: FOCH 12686
- Bioactive properties in camel milk: Kaskous, Shehadeh & Pfaffl, Michael. (2017). Bioactive Properties of Minor Camel Milk Ingredients-An Overview. Journal of Camel Practice and Research. 24. 15. 10.5958/2277-8934.2017.00003.0.
- 8 extremely allergic Kids given a trial period of camels milk. All 8 saw amazing results. Camel milk for food allergies in children. Shabo Y, Barzel R, Margoulis M, Yagil R. Isr Med Assoc J. 2005 Dec;7(12):796-8. PMID: 16382703
- Camel’s milk is not recognizable by any IgE antibodies even when the child is allergic to all other milks. CROSS-REACTIVITY BETWEEN MILK PROTEINS FROM DIFFERENT ANIMAL SPECIESP. Restani, A. Gaiaschi, A. Plebani*, B. Beretta, G. Cavagni^, A. Fiocchi**, C. PoiesiI, T. Velona, A.G. Ubazio* and C.L. Galli Laboratory Toxicology, Institute of Pharmacological Sciences, University of Milan, Milan, *Department of Paediarics, University of Brescia, ^Dept. of Paediatrics, Sassuolog and **San Paolo Biomedial Institute of Milan Clinical and Experimental Allergy, 1999, Volume 29, 997-1004
- Camel milk for food allergies in children. Shabo Y, Barzel R, Margoulis M, Yagil R. Isr Med Assoc J. 2005 Dec;7(12):796-8. PMID: 16382703
- Hu Z, Chang X, Pan Q, Gu K, Okechukwu PN. Gastroprotective and Ulcer Healing Effects of Camel Milk and Urine in HCl/EtOH, Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (Indomethacin), and Water-Restraint Stress-induced Ulcer in Rats. Pharmacognosy Magazine. 2017;13(52):559-565. doi:10.4103/pm.pm_135_17.
- Maswadeh HM, Aljarbou AN, Alorainy MS, Alsharidah MS, Khan MA. Etoposide Incorporated into Camel Milk Phospholipids Liposomes Shows Increased Activity against Fibrosarcoma in a Mouse Model. BioMed Research International. 2015;2015:743051. doi:10.1155/2015/743051.




No Comments